What is CVD Diamond?

CVD DIAMOND is a polycrystalline diamond synthesized from diamond crystals with a diameter of 10 to 30 nanometers.

Previously, due to the nitrogen atoms in the air entering the diamond crystals, the artificial diamonds have a light sugar color. After the scientists improved the production method, the artificial diamonds produced have no difference in appearance from natural diamonds.
Due to the different natural environments, the molecular structure of an artificial diamond is not a complete octahedral structure of natural diamond but a complex structure, which will produce phosphorescence. With the maturity of artificial diamond production technology, its cost is low, and it can make diamonds of various colors to emerge in the jewelry market. Although synthetic diamonds from laboratories or factories have been around for decades, artificial diamonds with gem-quality have only appeared in recent years. Originally, artificial diamonds were mainly used for industrial purposes such as cutting tools but also used in jewelry.
The Law of Fair Trade requires man-made diamond dealers to truthfully state their quality at the time of sale, and use generally accepted terms to describe, such as "man-made", "man-made" or "laboratory-made". Almost all man-made diamonds are of type Ib, and this type accounts for less than two percent of natural diamonds. There is a very inexpensive device that can verify Ib-type diamonds, but to determine whether a diamond is artificially synthesized, it relies on testing by a qualified gemstone laboratory.
Effect of CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) Diamond
-
Subversion of the values of diamonds
In the past, expensive diamonds, which claimed to be crystallized in millions of years, can be manufactured in the laboratory in less than a week, subverting the general value of diamonds. -
Enhance the application of diamonds in various fields
In the past, diamonds were mostly used as jewelry because of their high prices. Once high-quality diamonds can be produced cheaply, their application value will quickly spread to various fields. Experts predict that the most important invention in the 21st century will be diamonds that will grow up. One day, cheap diamonds will replace the role of silicon in semiconductors, allowing human technology to enter another world.
After the mass production of diamonds, they can be more affordable and have more diversified functions. Diamonds have high hardness, excellent thermal conductivity, cutting, and grinding characteristics, and can be used in medical and electronic components.
What is Moissanite?
Moissanite is naturally occurring silicon carbide and its various crystalline polymorphs. It has the chemical formula SiC and is a rare mineral, discovered by the French chemist Henri Moissan in 1893. Silicon carbide is useful for commercial and industrial applications due to its hardness, optical properties and thermal conductivity.
Silicon carbide is a superhard material with a hardness of 9.25, slightly lower than diamonds. The refractive index is slightly higher than the diamond (2.648 ~ 2.691), and the dispersion is also good (0.104). Compared with other materials, its thermal conductivity is 2.3-4.9 watt/K-cm, which is close to the diamond's 26 watt/K-cm. The price of synthetic silicon carbide is one-tenth of diamonds, so it is considered a good substitute for diamonds. Silicon carbide crystals and films have many industrial uses. Large particles of silicon carbide single crystal can be used to produce jewelry (imitation diamonds).
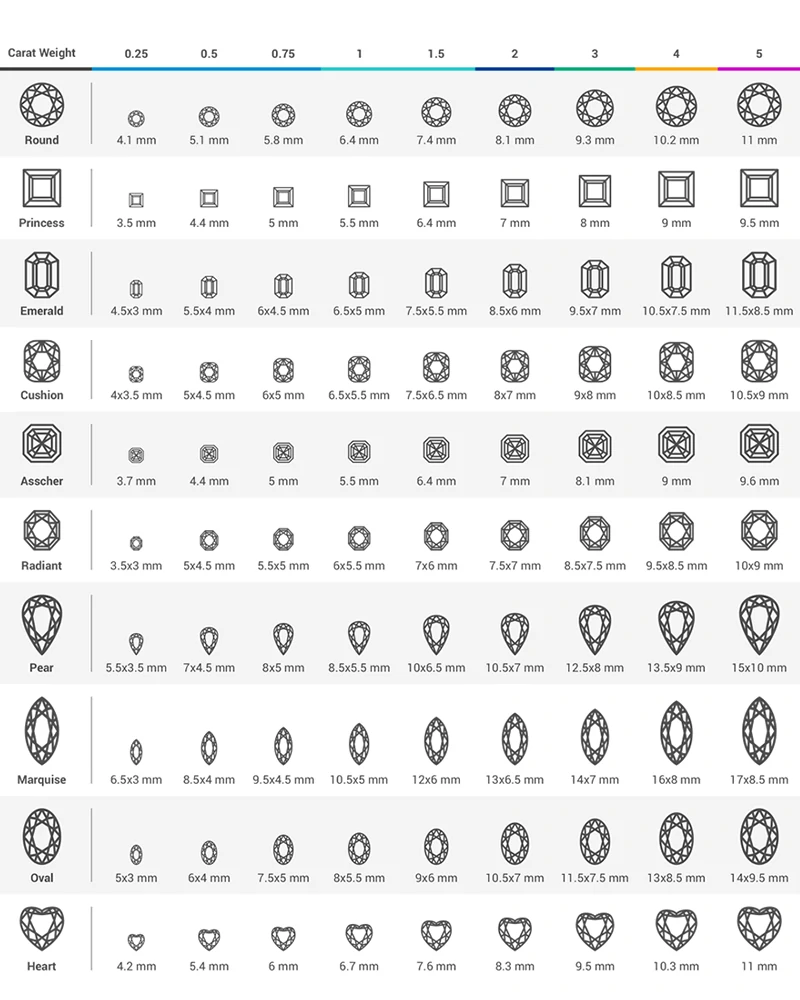
Diamond Carat and Size